-
Table of Contents
« Boostez votre santé avec l’IGF-1 et l’insuline : une combinaison gagnante pour une vie équilibrée. »
Introduction
Soutien de l’IGF-1 grâce à l’insuline est un processus biologique important dans le corps humain. L’IGF-1, ou facteur de croissance analogue à l’insuline, est une hormone qui joue un rôle crucial dans la croissance et le développement des cellules. L’insuline, quant à elle, est une hormone produite par le pancréas qui régule le taux de sucre dans le sang. Ensemble, ces deux hormones travaillent en étroite collaboration pour soutenir la croissance et le maintien des tissus et des organes du corps. Dans cet article, nous allons explorer le lien entre l’insuline et l’IGF-1 et comprendre comment ils fonctionnent ensemble pour maintenir un équilibre sain dans le corps.
The Role of Insulin in Supporting IGF-1 Production
Insulin and IGF-1 are two important hormones that play crucial roles in the human body. While insulin is primarily known for its role in regulating blood sugar levels, it also has a significant impact on the production of IGF-1. In this article, we will explore the relationship between insulin and IGF-1 and how insulin supports the production of this essential hormone.
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate the amount of glucose in the blood. When we eat, our body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. In response, the pancreas releases insulin to help transport glucose from the blood into the cells, where it can be used for energy or stored for later use.
IGF-1, or insulin-like growth factor 1, is a hormone that is primarily produced in the liver. It plays a crucial role in growth and development, as well as maintaining healthy bones and muscles. IGF-1 is also known to have anti-aging effects and is essential for tissue repair and regeneration.
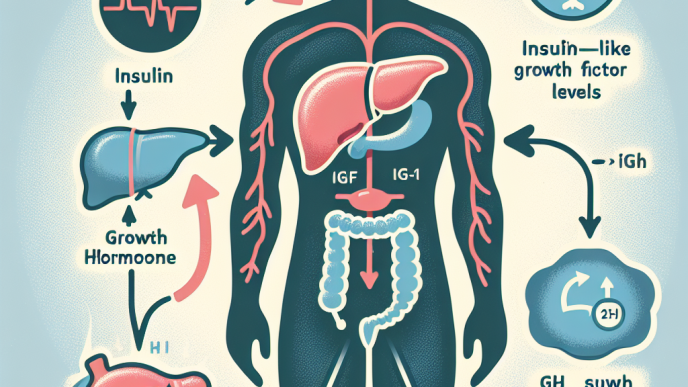
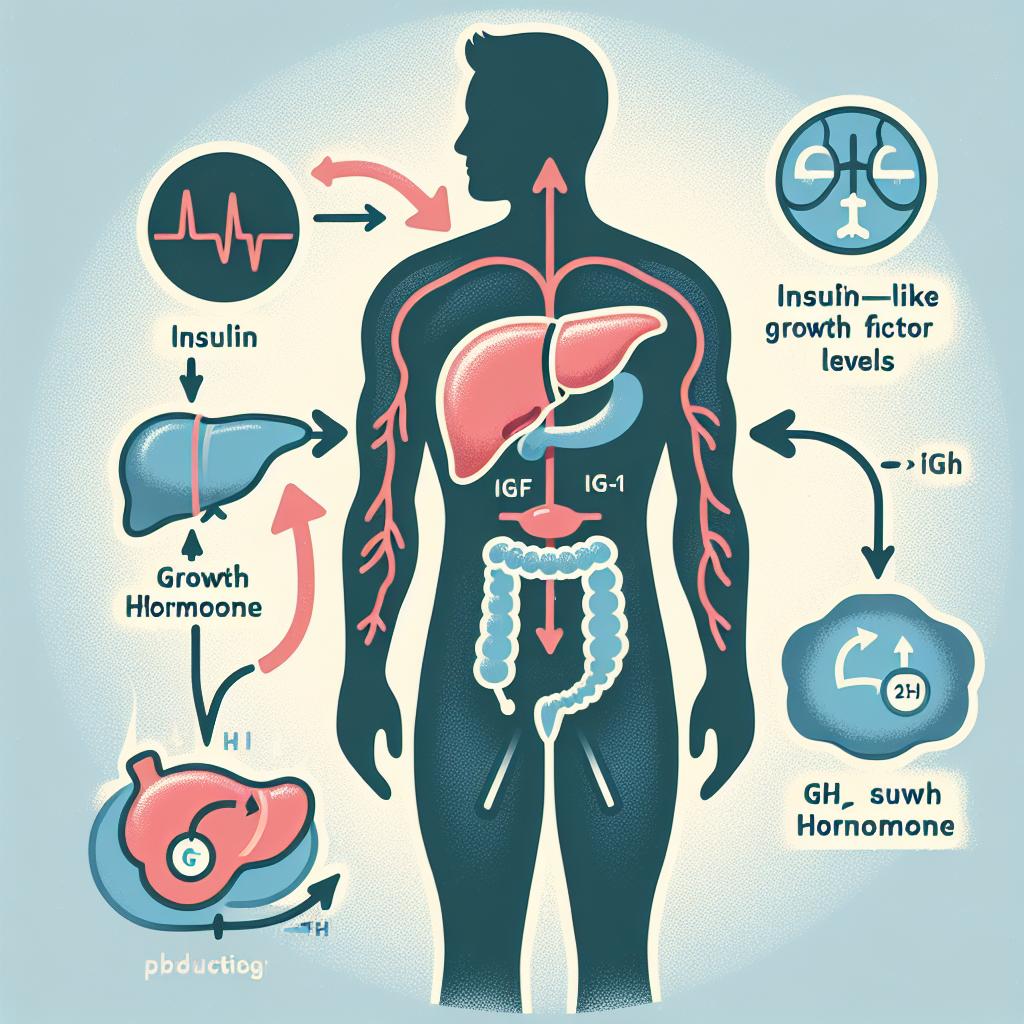
The production of IGF-1 is regulated by various factors, including nutrition, exercise, and hormones. One of the key hormones that influence IGF-1 production is insulin. Insulin and IGF-1 have a close relationship, and their levels in the body are closely linked.
Insulin stimulates the production of IGF-1 by increasing the expression of IGF-1 genes in the liver. This means that when insulin levels are high, the liver produces more IGF-1. On the other hand, when insulin levels are low, IGF-1 production is reduced.
One of the ways insulin supports IGF-1 production is by increasing the availability of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. IGF-1 is a protein hormone, and it requires amino acids to be produced. Insulin helps transport amino acids into the cells, where they can be used for protein synthesis, including the production of IGF-1.
Insulin also plays a role in regulating the activity of growth hormone (GH), which is another hormone that influences IGF-1 production. GH is produced by the pituitary gland and stimulates the liver to produce IGF-1. However, GH can only exert its effects when insulin levels are low. This is because insulin inhibits the release of GH from the pituitary gland. Therefore, when insulin levels are high, GH levels are low, and IGF-1 production is reduced.
Furthermore, insulin also helps regulate the activity of IGF-binding proteins (IGFBPs). These proteins bind to IGF-1 and regulate its availability and activity in the body. Insulin increases the production of IGFBPs, which in turn, increases the amount of IGF-1 available for use.
The relationship between insulin and IGF-1 is not one-sided. IGF-1 also has an impact on insulin sensitivity, which is the body’s ability to respond to insulin. Studies have shown that IGF-1 can improve insulin sensitivity, which means that the body requires less insulin to transport glucose into the cells. This is beneficial for individuals with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes.
In addition to its role in supporting IGF-1 production, insulin also has a direct impact on bone and muscle health. Both insulin and IGF-1 are essential for bone growth and maintenance. Insulin stimulates the production of osteoblasts, which are cells responsible for bone formation. IGF-1, on the other hand, promotes the differentiation of osteoblasts into mature bone cells.
Similarly, both insulin and IGF-1 play a role in muscle growth and repair. Insulin helps transport glucose and amino acids into muscle cells, where they can be used for energy and protein synthesis. IGF-1, on the other hand, stimulates the growth and repair of muscle tissue.
In conclusion, insulin plays a crucial role in supporting the production of IGF-1. It does so by increasing the availability of amino acids, regulating the activity of GH and IGFBPs, and improving insulin sensitivity. The close relationship between these two hormones highlights the importance of maintaining healthy insulin levels for overall health and well-being.
Understanding the Relationship Between Insulin and IGF-1 for Optimal Health
Insulin and IGF-1 are two important hormones that play crucial roles in maintaining optimal health. While insulin is primarily known for its role in regulating blood sugar levels, IGF-1 is often associated with growth and development. However, these two hormones are closely interconnected and work together to support various bodily functions.
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas in response to the rise in blood sugar levels after a meal. Its main function is to facilitate the uptake of glucose from the bloodstream into the cells, where it can be used for energy or stored for later use. Without insulin, the body would not be able to properly regulate blood sugar levels, leading to a condition known as diabetes.
On the other hand, IGF-1, or insulin-like growth factor 1, is a hormone produced by the liver in response to growth hormone stimulation. It plays a crucial role in promoting cell growth and division, particularly in bone, muscle, and other tissues. IGF-1 also has an important role in regulating metabolism, immune function, and brain development.
While insulin and IGF-1 have distinct functions, they are closely related and have a significant impact on each other’s levels and actions in the body. Insulin is known to stimulate the production of IGF-1, and in turn, IGF-1 can enhance the effects of insulin. This relationship between the two hormones is essential for maintaining optimal health.
One of the key ways in which insulin and IGF-1 work together is in regulating blood sugar levels. Insulin helps to lower blood sugar levels by promoting the uptake of glucose into cells, while IGF-1 helps to maintain stable blood sugar levels by promoting the production of new cells that can use glucose for energy. This balance between insulin and IGF-1 is crucial for preventing conditions such as diabetes and maintaining overall metabolic health.
Moreover, insulin and IGF-1 also play a significant role in muscle growth and maintenance. Insulin promotes the uptake of amino acids, the building blocks of protein, into muscle cells, while IGF-1 stimulates the growth and repair of muscle tissue. This synergy between the two hormones is essential for maintaining muscle mass and strength, particularly in older adults who may experience a decline in IGF-1 levels.
In addition to their roles in metabolism and muscle growth, insulin and IGF-1 also have important effects on brain function. Insulin receptors are found in high concentrations in the brain, and insulin plays a crucial role in regulating brain glucose metabolism. IGF-1, on the other hand, has been shown to promote the growth and survival of brain cells, as well as enhance cognitive function. This highlights the importance of maintaining balanced levels of both hormones for optimal brain health.
Furthermore, insulin and IGF-1 also have a significant impact on the immune system. Insulin has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects, while IGF-1 plays a role in promoting the production of immune cells. This interplay between the two hormones is crucial for maintaining a healthy immune response and protecting the body from infections and diseases.
In conclusion, insulin and IGF-1 are two hormones that work closely together to support various bodily functions. While insulin is primarily known for its role in regulating blood sugar levels, IGF-1 plays a crucial role in growth, metabolism, brain function, and immune response. Maintaining a balance between these two hormones is essential for optimal health and preventing various health conditions. Therefore, it is important to support the production and actions of both insulin and IGF-1 through a healthy diet, regular exercise, and proper management of any underlying health conditions.
Maximizing IGF-1 Support through Insulin Regulation: Tips and Strategies
Insulin and IGF-1 are two important hormones that play crucial roles in our body’s growth and development. While insulin is primarily known for its role in regulating blood sugar levels, it also has a significant impact on the production and function of IGF-1. In this article, we will explore the relationship between insulin and IGF-1 and discuss tips and strategies for maximizing IGF-1 support through insulin regulation.
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate the amount of glucose in our blood. When we eat, our body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. In response, the pancreas releases insulin to help transport glucose from the blood into our cells, where it can be used for energy or stored for later use. Without insulin, our cells would not be able to absorb glucose, leading to high blood sugar levels and potentially serious health complications.
On the other hand, IGF-1 (Insulin-like Growth Factor 1) is a hormone produced by the liver that plays a crucial role in promoting growth and development in our body. It is often referred to as the « growth hormone » because it stimulates the growth of bones, muscles, and other tissues. IGF-1 also has a role in regulating metabolism, promoting cell growth and repair, and supporting the immune system.
The relationship between insulin and IGF-1 is closely intertwined. Insulin is necessary for the production of IGF-1, and without adequate insulin levels, the body may not be able to produce enough IGF-1. This can lead to a deficiency in IGF-1, which can have significant consequences on our health. Low levels of IGF-1 have been linked to decreased muscle mass, increased body fat, and a higher risk of developing chronic diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
So, how can we maximize IGF-1 support through insulin regulation? The first step is to maintain healthy insulin levels. This can be achieved through a balanced diet and regular exercise. Consuming a diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods and limiting sugary and high-carbohydrate foods can help regulate insulin levels. Regular exercise also helps improve insulin sensitivity, allowing our cells to use insulin more efficiently.
Another important factor in maximizing IGF-1 support is getting enough sleep. Studies have shown that inadequate sleep can disrupt insulin production and lead to insulin resistance, which can ultimately affect IGF-1 levels. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support healthy insulin levels and promote the production of IGF-1.
In addition to lifestyle factors, there are also supplements that can help regulate insulin levels and support the production of IGF-1. One such supplement is alpha-lipoic acid (ALA), a powerful antioxidant that has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and promote the production of IGF-1. Other supplements that may support insulin regulation and IGF-1 production include chromium, magnesium, and vitamin D.
It is also essential to manage stress levels to support healthy insulin and IGF-1 levels. Chronic stress can lead to increased cortisol levels, which can disrupt insulin production and lead to insulin resistance. Finding ways to manage stress, such as through meditation, exercise, or therapy, can help support healthy insulin levels and promote the production of IGF-1.
In conclusion, insulin and IGF-1 are two crucial hormones that work together to support our body’s growth and development. By maintaining healthy insulin levels through diet, exercise, and lifestyle habits, we can support the production of IGF-1 and promote overall health and well-being. Additionally, incorporating supplements and stress management techniques can further support insulin regulation and maximize IGF-1 support. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your diet or supplement regimen. With proper care and attention, we can optimize our body’s natural production of IGF-1 and support our overall health and vitality.
Q&A
1) Qu’est-ce que le soutien de l’IGF-1 grâce à l’insuline ?
Le soutien de l’IGF-1 grâce à l’insuline est une méthode utilisée pour augmenter les niveaux d’IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor 1) dans le corps en utilisant de l’insuline. L’IGF-1 est une hormone de croissance qui joue un rôle important dans la croissance et la réparation des tissus musculaires et osseux.
2) Pourquoi utilise-t-on l’insuline pour soutenir l’IGF-1 ?
L’insuline est utilisée pour soutenir l’IGF-1 car elle stimule la production de cette hormone de croissance par le foie. En augmentant les niveaux d’IGF-1, on peut favoriser la croissance musculaire et osseuse, ainsi que la récupération après un entraînement intense.
3) Quels sont les avantages du soutien de l’IGF-1 grâce à l’insuline ?
Les avantages du soutien de l’IGF-1 grâce à l’insuline incluent une augmentation de la masse musculaire, une amélioration de la force et de la performance physique, une meilleure récupération après l’exercice, ainsi qu’une amélioration de la santé des os et des articulations. Cela peut également être bénéfique pour les personnes souffrant de troubles musculaires ou osseux tels que la dystrophie musculaire ou l’ostéoporose. Cependant, il est important de noter que l’utilisation de l’insuline pour soutenir l’IGF-1 doit être supervisée par un professionnel de la santé et ne doit pas être utilisée sans consultation médicale préalable.